本文最后更新于 2024年11月11日 上午
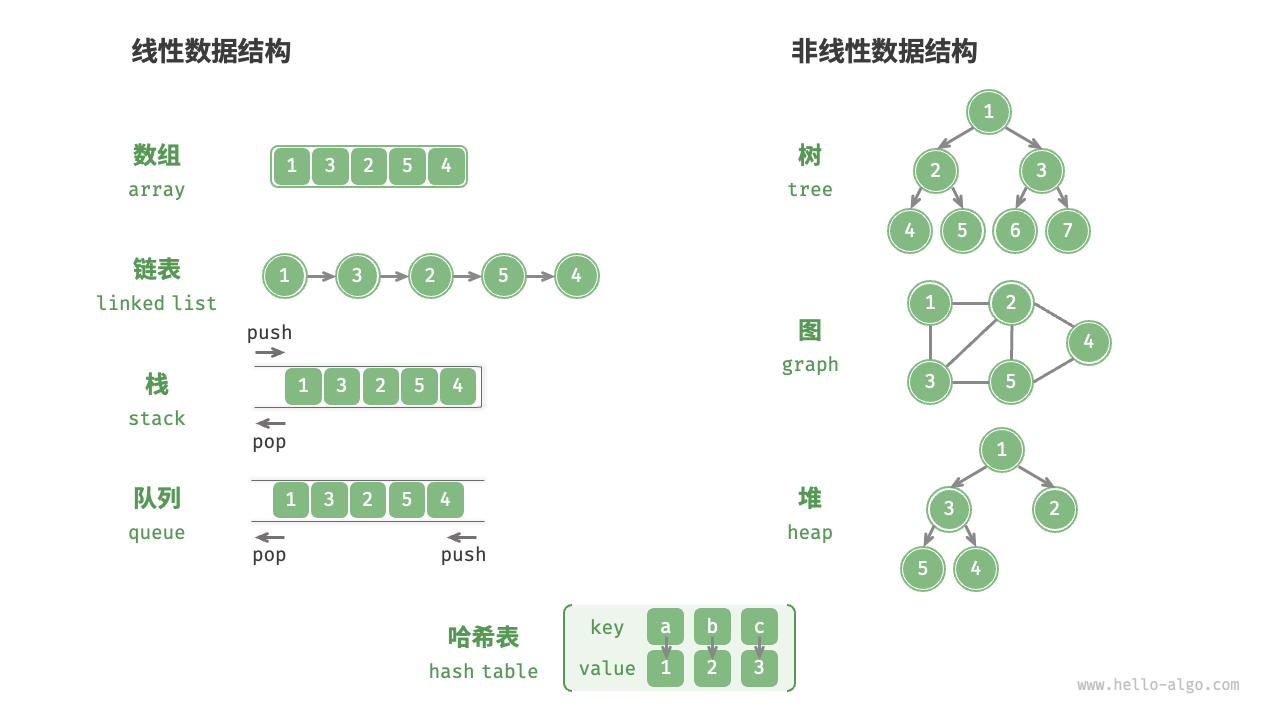
数据结构
数据结构由 数据 和 结构 两部分组成。我们主要讨论的是后者,即结构部分。
按照 逻辑结构 可以将其区分为 线性结构 和 非线性结构 。
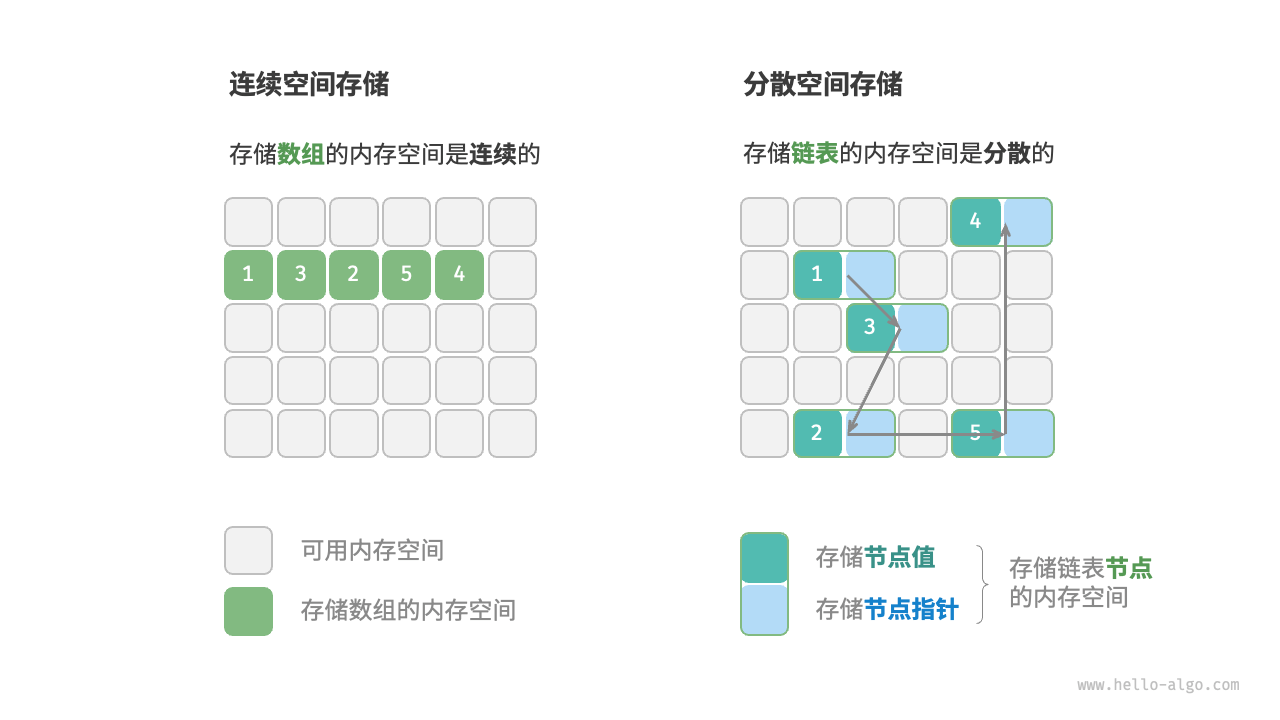
按照 物理结构 可以将其区分为 连续结构 和 分散结构 。
【模板】双链表
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/829/
思路:用两个空结点作为起始状态的边界,避免所有边界讨论。
时间复杂度:插入、删除结点均为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using ll = long long ;using namespace std;template <class T >class myList {private :int idx;int > left, right;public :myList (const int n) {2 ;resize (n + 10 );resize (n + 10 );resize (n + 10 );1 ] = 0 , right[0 ] = 1 ;void push_back (T x) insert_left (1 , x);void push_front (T x) insert_right (0 , x);void insert_left (int k, T x) insert_right (left[k], x);void insert_right (int k, T x) void erase (int k) void output () for (int i = right[0 ]; i != 1 ; i = right[i]) {" \n" [i == 1 ];void solve () int n;myList<int > ls (n) ;while (n--) {int k, x;if (op == "L" ) {push_front (x);else if (op == "R" ) {push_back (x);else if (op == "D" ) {erase (k + 1 );else if (op == "IL" ) {insert_left (k + 1 , x);else {insert_right (k + 1 , x);output ();signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 import heapqfrom collections import defaultdictfrom typing import List , Tuple import mathfrom itertools import combinationslambda : int (input ())lambda : float (input ())lambda : tuple (map (int , input ().split()))lambda : list (map (int , input ().split()))class myList :def __init__ (self, n: int ) -> None :self .val = [0 ] * (n + 10 )self .left = [0 ] * (n + 10 )self .right = [0 ] * (n + 10 )self .idx = 2 self .right[0 ] = 1 self .left[1 ] = 0 def push_front (self, x: int ):self .insert_right(0 , x)def push_back (self, x: int ):self .insert_left(1 , x)def insert_left (self, k: int , x: int ):self .insert_right(self .left[k], x)def insert_right (self, k: int , x: int ):self .val[self .idx] = xself .right[self .idx] = self .right[k]self .left[self .right[k]] = self .idxself .left[self .idx] = kself .right[k] = self .idxself .idx += 1 def erase (self, k: int ):self .left[self .right[k]] = self .left[k]self .right[self .left[k]] = self .right[k]def output (self ) -> None :self .right[0 ]while i != 1 :print (self .val[i], end=' ' )self .right[i]def solve () -> None :for _ in range (n):input ().split()if op[0 ] == 'L' :int (op[-1 ]))elif op[0 ] == 'R' :int (op[-1 ]))elif op[0 ] == 'D' :int (op[-1 ]) + 1 )elif op[0 ] == 'IL' :int (op[1 ]) + 1 , int (op[-1 ]))else :int (op[1 ]) + 1 , int (op[-1 ]))if __name__ == '__main__' :1 while T: solve(); T -= 1
【模板】单调栈
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/832/
题意:对于一个序列中的每一个元素,寻找每一个元素左侧最近的比其小的元素。
思路一:暴力枚举
显然对于每一个元素 nums[i],我们可以枚举倒序 [0, i-1] 直到找到第一个 nums[j] < nums[i]
时间复杂度:O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
思路二:单调栈
可以发现时间开销主要在倒序枚举上,我们能少枚举一些元素吗?答案是可以的。我们定义「寻找 [i-1, 0] 中比当前元素小的第一个元素」的行为叫做「寻找合法对象」。显然我们在枚举每一个元素时都需要 查询 和 维护 这样的合法对象线性序列,可以理解为记忆化从而加速查询。那么如何高效查询和维护这样的线性序列呢?不妨考虑每一个合法对象对曾经的合法对象的影响:
若当前元素 nums[i] 可以成为后续 [i+1, n-1] 元素的合法对象。则从 i-1 开始一直往左,只要比当前大的元素,都不可能成为 [i+1, n-1] 的合法对象,肯定都被 nums[i] “拦住了”。那么在「合法对象序列」中插入当前合法对象之前,需要不断尾弹出比当前大的元素
若当前元素 nums[i] 不能成为后续 [i+1, n-1] 元素的合法对象。表明当前元素过大,此时就不用将当前元素插入「合法对象序列」
经过上述两个角度的讨论,很容易发现这样维护出来的的合法序列是严格单调递增的。于是,在查询操作时仅需要进行尾比较与尾弹出即可,在维护操作时,仅需要尾插入即可。满足这样的线性数据结构有很多,如栈、队列、数组、链表,我们就使用栈来演示,与标题遥相呼应
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using ll = long long ;using namespace std;void solve () int n;vector<int > a (n) ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int > s;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {while (s.size () && s.top () >= a[i]) {pop ();size () ? s.top () : -1 ) << " " ;push (a[i]);signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
相似题:
下一个更大元素 II
【模板】单调队列
标签:双端队列、滑动窗口、单调队列
题意:给定一个含有 n 个元素的序列,求解其中每个长度为 k 的子数组中的最值。
思路:显然我们可以 O ( n k ) O(nk) O ( nk ) O ( k ) O(k) O ( k ) O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 )
插入元素到队尾:此时和单调栈的逻辑类似。如果当前元素可以作为当前子数组或后续子数组的最小值,则需要从当前队尾开始依次弹出比当前元素严格大的元素,最后再将当前元素入队。注意 :当遇到和当前元素值相等的元素时不能出队,因为每一个元素都会经历入队和出队的操作,一旦此时出队了,后续进行出队判定时会提前弹出本不应该出队的与其等值的元素。
弹出队头元素:如果队头元素和子数组左端点 nums[i-k] 的元素值相等,则弹出。
获得队头元素:O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 )
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using ll = long long ;using namespace std;template <class T >struct minQueue {void pushBack (T x) while (q.size () && x < q.back ()) {pop_back ();push_back (x);void popFront (T x) if (q.size () && q.front () == x) {pop_front ();T getMinValue () {return q.front ();template <class T >struct maxQueue {void pushBack (T x) while (q.size () && x > q.back ()) {pop_back ();push_back (x);void popFront (T x) if (q.size () && q.front () == x) {pop_front ();T getMaxValue () {return q.front ();void solve () int n, k;vector<int > nums (n) ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int > minq;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {pushBack (nums[i]);if (i >= k) {popFront (nums[i - k]);if (i >= k - 1 ) {getMinValue () << " \n" [i == n - 1 ];int > maxq;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {pushBack (nums[i]);if (i >= k) {popFront (nums[i - k]);if (i >= k - 1 ) {getMaxValue () << " \n" [i == n - 1 ];signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 from collections import defaultdict, dequefrom typing import List , Tuple from itertools import combinations, permutationsimport math, heapq, queuelambda : int (input ())lambda : float (input ())lambda : tuple (map (int , input ().split()))lambda : list (map (int , input ().split()))def solve () -> None :for i in range (n):while len (qa) and nums[i] < qa[-1 ]:while len (qb) and nums[i] > qb[-1 ]:if i >= k:if len (qa) and qa[0 ] == nums[i - k]:if len (qb) and qb[0 ] == nums[i - k]:if i >= k - 1 :0 ])0 ])print (' ' .join(map (str , ra)))print (' ' .join(map (str , rb)))if __name__ == '__main__' :1 while T: solve(); T -= 1
【模板】最近公共祖先
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3379
题意:寻找树中指定两个结点的最近公共祖先 (Lowest Common Ancestor, 简称 LCA) \text{(Lowest Common Ancestor, 简称 LCA)} (Lowest Common Ancestor, 简称 LCA)
思路:对于每次查询,我们可以从指定的两个结点开始往上跳,第一个公共结点就是目标的 LCA,每一次询问的时间复杂度均为 O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) fa[i][j] 数组,表示 i i i 2 j 2^j 2 j O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
预处理:可以发现,对于 fa[i][j],我们可以通过递推的方式获得,即 fa[i][j] = fa[fa[i][j-1]][j-1],当前结点向上跳跃 2 j 2^j 2 j 2 j − 1 2^{j-1} 2 j − 1 2 j − 1 2^{j-1} 2 j − 1 o r or or f a fa f a
跳跃:我们首先需要将两个结点按照倍增的思路向上跳到同一个深度,接下来两个结点同时按照倍增的思路向上跳跃,为了确保求出最近的,我们需要确保在跳跃的步调一致的情况下,两者的祖先始终不相同,那么倍增结束后,两者的父结点就是最近公共祖先,即 fa[x][k] 或 fa[y][k]
时间复杂度:Θ ( n log n + m log n ) \Theta(n \log n + m \log n) Θ ( n log n + m log n )
n log n n \log n n log n m log n m \log n m log n m m m
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 const int N = 5e5 + 10 ;int n, Q, root;int > G[N];int fa[N][20 ], dep[N];int > q;void init () 1 ;push (root);while (q.size ()) {int now = q.front ();pop ();for (int ch: G[now]) {if (!dep[ch]) {1 ;0 ] = now;for (int k = 1 ; k <= 19 ; k++) {-1 ] ][k-1 ];push (ch);int lca (int a, int b) if (dep[a] < dep[b]) swap (a, b);for (int k = 19 ; k >= 0 ; k--)if (dep[fa[a][k]] >= dep[b])if (a == b) return a;for (int k = 19 ; k >= 0 ; k--)if (fa[a][k] != fa[b][k])return fa[a][0 ];void solve () for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; ++i) {int a, b;push_back (b);push_back (a);init ();while (Q--) {int a, b;lca (a, b) << "\n" ;
【栈】验证栈序列
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4387
题意:给定入栈序列与出栈序列,问出栈序列是否合法
思路:思路很简单,就是对于当前出栈的数,和入栈序列中最后已出栈的数之间,如果还有数没有出,那么就是不合法的出栈序列,反之合法。这是从入栈的结果来看的,如果这么判断就需要扫描入栈序列 n 次,时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
抽象总结上述思路:为了判断出栈序列是否合法,我们不妨思考:对于每一个出栈的数,出栈的时机是什么?可以发现出栈的时机无非两种:
一入栈就出栈(对应于枚举待入栈序列时发现待入栈的数与出栈序列队头相等)
紧跟着刚出栈的数继续出栈(对应于枚举待入栈序列时发现待入栈的数与出栈序列队头相等之后,继续判断出栈序列队头与已入栈的数是否相等,若相等则不断判断并出栈)
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> #include <unordered_map> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std;void solve () int n;vector<int > a (n) , b (n) ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) cin >> b[i];int > stk;int i = 0 , j = 0 ;while (i < n) {if (a[i] != b[j]) stk.push (a[i++]);else {while (!stk.empty () && b[j] == stk.top ()) {pop ();empty () ? "Yes" : "No" ) << "\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
二叉搜索树 & 平衡树
如果我们想要在 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n ) 二叉搜索树 (Binary Search Tree) 这一数据结构。然而,在某些极端的情况下,例如当插入的数据是单调不减或不增时,这棵树就会退化为一条链从而导致所有的增删查改操作退化到 O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) 平衡二叉搜索树 (Balanced Binary Search Tree) 这一数据结构。
关于平衡二叉搜索树,有非常多的变种与实现,不同的应用场景会选择不同的平衡树类型。Treap 更灵活,通过随机化优先级实现预期的平衡,但在最坏情况下可能退化。AVL 树 严格保持平衡,保证了 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n ) 红黑树 通过较宽松的平衡条件实现了较好的插入和删除性能,通常被广泛用于需要高效插入删除操作的系统(如 STL 中的 map 和 set)。一般来说,红黑树是一个较为通用的选择,而在需要严格平衡性时,AVL 树可能是更好的选择。
Treap
Treap 是二叉搜索树和堆的结合体。它通过维护两种性质来保持平衡:
二叉搜索树性质 :每个节点的左子树的所有节点值小于该节点的值,右子树的所有节点值大于该节点的值。堆性质 :每个节点的优先级(通常随机生成)要大于或等于其子节点的优先级。
平衡机制 :
Treap 使用随机化优先级使得树的形状接近于理想的平衡树(期望树高为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
通过旋转操作(左旋和右旋)在插入和删除时保持堆的性质。
优点 :
实现相对简单。
由于随机化的优先级,在期望情况下,树的高度是 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
灵活性高,可以根据需要调整优先级函数。
缺点 :
最坏情况下,树的高度可能退化为 O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
AVL 树
AVL 树是最早发明的自平衡二叉搜索树之一,1962 年由 Adelson-Velsky 和 Landis 发明。
平衡因子 :每个节点的左右子树高度差不能超过 1 1 1
平衡机制 :
插入或删除节点后,如果某个节点的平衡因子不再为 − 1 -1 − 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
旋转操作包括:左旋转、右旋转、左右双旋转和右左双旋转。
优点 :
严格的平衡条件保证了树的高度始终为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n ) O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
缺点 :
由于平衡条件严格,每次插入和删除后可能需要较多的旋转操作,从而导致实现较复杂,插入和删除操作的常数时间开销较大。
红黑树
红黑树是一种较为宽松的自平衡二叉搜索树,由 Rudolf Bayer 于 1972 年发明。
颜色属性 :每个节点都有红色或黑色两种颜色,通过这些颜色约束树的平衡性。
平衡机制 :
通过遵循红黑树的五个性质来保持平衡:
每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色。
根节点是黑色。
叶子节点(NIL 节点)是黑色。
如果一个节点是红色的,那么它的子节点必须是黑色(红节点不能连续出现)。
从任一节点到其每个叶子节点的所有路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点。
插入和删除操作可能破坏红黑树的性质,需要通过重新着色和旋转来恢复平衡。
优点 :
红黑树的高度最多是 Θ ( 2 log n ) \Theta (2 \log n) Θ ( 2 log n ) O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
由于平衡条件较为宽松,插入和删除操作需要的旋转操作通常比 AVL 树少,效率更高。
缺点 :
实现较复杂,特别是插入和删除的平衡修复过程。
虽然红黑树的搜索效率与 AVL 树相似,但由于平衡条件较宽松,实际应用中的树高度通常略高于 AVL 树,因此搜索操作的效率稍低。
【二叉树】美国血统
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1827
题意:给定二叉树的中序和先序序列,输出后序序列
思路:经典二叉树的题目,主要用于巩固加强对于递归的理解。指针其实是没有必要的,为了得到后序序列,我们只需要有一个 dfs 序即可,为了得到 dfs 序,我们只需要根据给出的中序和前序序列即可得到 dfs 序
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
指针做法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 30 ;struct Node {char data;Node (char _data) : data (_data), le (nullptr ), ri (nullptr ) {}Node* build (int i, int j, int p, int q) {if (i > j) return nullptr ;new Node (pre[i]);int k; for (k = p; k <= q; k++)if (mid[k] == root->data)break ;build (i + 1 , k - p + i, p, k - 1 );build (k - p + i + 1 , j, k + 1 , q);return root;void solve () int i = 0 , j = pre.size () - 1 ;int p = 0 , q = mid.size () - 1 ;build (i, j, p, q);signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
构造出 dfs 序直接输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 30 ;void build (int i, int j, int p, int q) if (i > j) return ;char root = pre[i];int k;for (k = p; k <= q; k++)if (mid[k] == root)break ;build (i + 1 , k - p + i, p, k - 1 );build (k - p + i + 1 , j, k + 1 , q);void solve () int i = 0 , j = pre.size () - 1 ;int p = 0 , q = mid.size () - 1 ;build (i, j, p, q);signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【二叉树】新二叉树
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1305
题意:给定一棵二叉树的 n 个结点信息,分别为当前结点的数据信息、左孩子结点信息和右结点信息,输出这棵二叉树的前序序列
思路:我们首先将这棵二叉树构建出来,接着遍历输出前序序列即可。关键在于如何构建二叉树?我们使用数组存储二叉树,对于每一个树上结点,我们将数组中元素的索引存储为树上结点信息,每一个结点再存储左孩子与右孩子的信息
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;int n;char root;struct Node {char l, r;200 ];void pre (char now) if (now == '*' ) return ;pre (tree[now].l);pre (tree[now].r);void solve () for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {if (i == 1 ) root = s[0 ];0 ]].l = s[1 ];0 ]].r = s[2 ];pre (root);signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【二叉树】遍历问题
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1229
题意:给定一棵二叉树的前序序列与后序序列,问中序序列的可能情况有多少种
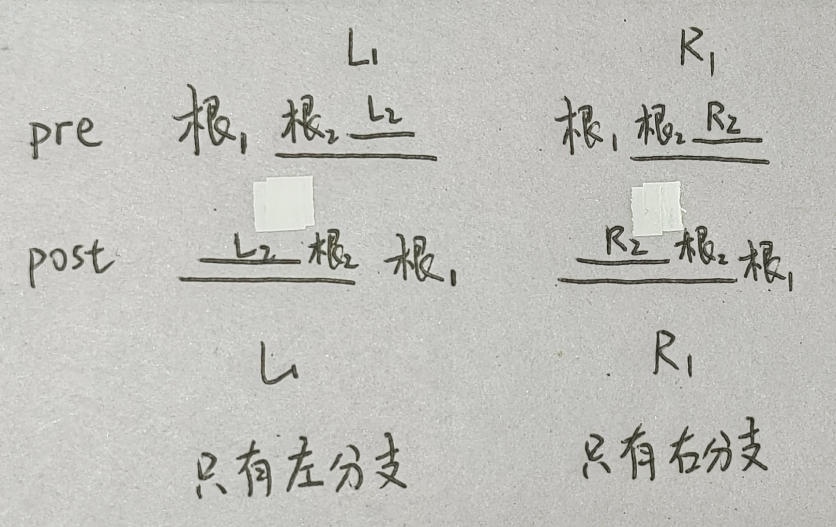
思路:我们采用从最小结构单元的思路进行考虑,即假设当前二叉树只有一个根结点与两个叶子结点,而非两棵子树。然后将题意进行等价变换,即问对于已经固定的前序和后序二叉树,该二叉树有多少种不同的形状?对于当前的最小结构二叉树,形状就是 左右根 or 根左右 ,现在的根可以直接确定,那么就只能从左右孩子进行变形,很显然只能进行左右交换的变形,但是问题是一旦左右变换,前序 or 后序都会变掉,说明这种左右孩子都存在的前后序固定的二叉树是唯一的,那么如何才是不唯一的呢?我们考虑减少孩子数量。假设没有孩子,那么很显然也只有一个形状,就是一个根结点,故排除。于是答案就呼之欲出了,就是当根结点只有一个孩子时,这个孩子无论是在左边还是右边,前后序都是相同的,但是中序序列就不同了,于是就产生了两种中序序列。于是最终的结论是:对于前后序确定的二叉树来说,中序序列的情况是就是 2 单分支结点数 2^{\text{单分支结点数}} 2 单分支结点数
如何寻找单分支结点呢?根据下面的递归图可以发现,无论是左单分支还是右单分支,如果 pre 的连续两个结点与 post 的连续两个结点对称相同,那么就一定有一个单分支结点,故只需要寻找前后序序列中连续两个字符对称相同的情况数 cnt 即可。最终的答案数就是 2 c n t 2^{cnt} 2 c n t
时间复杂度:O ( n m ) O(nm) O ( nm )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int cnt = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < pre.size () - 1 ; i++)for (int j = 0 ; j < post.size (); j++)if (pre[i] == post[j + 1 ] && pre[i + 1 ] == post[j])1 << cnt) << "\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【二叉树】医院设置 🔥
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1364
题意:给定一棵二叉树,树中每一个结点存储了一个数值表示一个医院的人数,现在需要在所有的结点中将一个结点设置为医院使得其余结点中的所有人到达该医院走的路总和最小。路程为结点到医院的最短路,边权均为 1。给出最终的最短路径总和
思路一:暴力
思路二:带权树的重心
暴力代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int n;int > G[N];int cnt[N];int bfs (int v) int res = 0 ;vector<bool > vis (n + 1 , false ) ;vector<int > d (n + 1 , 0 ) ; int > q;true ;0 ;push (v);while (q.size ()) {int now = q.front ();pop ();for (auto & ch: G[now]) {if (!vis[ch]) {true ;1 ;push (ch);return res;void solve () for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {int count, l, r;if (l) {push_back (l);push_back (i);if (r) {push_back (r);push_back (i);int res = 1e7 + 10 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {min (res, bfs (i));"\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
优化代码
【二叉树】二叉树深度
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4913
题意:给定一棵二叉树,求解这棵二叉树的深度
思路:有两个考点,一个是如何根据给定的信息(从根结点开始依次给出已存在树上结点的左右孩子的编号)构建二叉树,一个是如何求解已经构建好的二叉树的深度。对于构建二叉树,我们沿用 T5 数组模拟构建的思路,直接定义结点类型即可;对于求解深度,很显然的一个递归求解,即左右子树深度值 +1 即可
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int n;struct Node {int l, r;int dep (int now) if (!now) return 0 ;return max (dep (t[now].l), dep (t[now].r)) + 1 ;void solve () for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {int x, y;dep (1 );signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【完全二叉树】淘汰赛
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1364
题意:给定 2 n 2^n 2 n
思路:很显然的一个完全二叉树的题目。我们都不需要进行递归操作,直接利用完全二叉树的下标性质利用数组模拟循环计算即可。给出的信息就是完全二叉树的全部叶子结点的信息,分别为球队编号 id 与球队能力值 val,我们从第 n-1 个结点开始循环枚举到第 1 个结点计算每一轮的胜者信息,最终输出最后一场的能力值较小者球队编号即可
时间复杂度:Θ ( 2 n ) \Theta(2n) Θ ( 2 n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 1 << 8 ;struct Node {int id, val;int n;void solve () 1 << n;for (int i = n; i <= 2 * n - 1 ; i++) {1 ;for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 1 ; i--)if (a[i * 2 ].val > a[i * 2 + 1 ].val) a[i] = a[i * 2 ];else a[i] = a[i * 2 + 1 ];if (a[2 ].val > a[3 ].val) cout << a[3 ].id;else cout << a[2 ].id;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【二叉树/LCA】二叉树问题
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3884
题意:给定一棵二叉树的结点关系信息,求出这棵二叉树的深度、宽度和两个指定结点之间的最短路径长度
思路:二叉树的构建直接采用有向图的构造方法。深度直接 dfs 即可,宽度直接在 dfs 遍历时哈希深度值即可。问题的关键在于如何求解两个给定结点之间的路径长度,很显然需要求解两个结点的 LCA,由于结点数 ≤ 100 \le 100 ≤ 100
length = 2 × ( d x − d l c a ) + ( d y − d l c a ) \text{length} = 2 \times (d_x - d_{lca}) + (d_y - d_{lca})
length = 2 × ( d x − d l c a ) + ( d y − d l c a )
其中 d i d_i d i i i i
时间复杂度:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int n, x, y;int > G[N];int depth, width;int , int > ha; int d[N]; int > temp, rx, ry; void dfs (int now, int level) max (depth, level);push_back (now);if (now == x) rx = temp;if (now == y) ry = temp;1 ;for (auto & ch: G[now]) {dfs (ch, level + 1 );pop_back ();int len (int x, int y) int i = 0 ;while (i < rx.size () && i < ry.size () && rx[i] == ry[i]) i++;int lca = rx[--i];return 2 * (d[x] - d[lca]) + (d[y] - d[lca]);void solve () for (int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i++) {int a, b;push_back (b);dfs (1 , 1 );"\n" ;for (auto & item: ha) width = max (width, item.second);"\n" ;len (x, y) << "\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【set】营业额统计
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2234
题意:给定一个序列 a,需要计算 a 1 + ∑ i = 2 , 1 ≤ j < i n min ∣ a i − a j ∣ a_1 + \displaystyle \sum_{i=2,1 \le j <i}^{n} \min {|a_i - a_j|} a 1 + i = 2 , 1 ≤ j < i ∑ n min ∣ a i − a j ∣
思路:很显然的思路,对于每一个数,我们需要对之前的序列在短时间内找到一个数值最接近当前数的数。
TLE:一开始的思路是每次对之前的序列进行排序,然后二分查找与当前值匹配的数,为了确保所有的情况都找到,就直接判断二分查到的数,查到的数之前的一个数,之后的一个数,但是时间复杂度极高(我居然没想到),是 O ( n 2 log n ) O(n^2 \log n) O ( n 2 log n )
AC:后来看了题解才知道 set 的正确用法,就是一个 平衡树的 STL 。我们对于之前的序列不断的插入平衡树中(默认升序排序),每次利用 s.lower_bound(x) 返回「集合 s 中第一个 ≥ \ge ≥ lower_bound() 的时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
当前数比集合中所有的数都大,那么 lower_bound 就会返回 s.end() 答案就是当前数与集合中最后一个数的差值
当前数比集合中所有的数都小,那么 lower_bound 就会返回 s.bigin() 答案就是集合中第一个数与当前数的差值
当前数存在于集合中 or 集合中既有比当前数大的又有比当前数小的,那么就比较查到的数与查到的数前一个数和当前数的差值,取最小的差值即可
时间复杂度:O ( n log n ) O(n \log n) O ( n log n )
TLE 但逻辑清晰代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1 << 16 ;int n, a[N];void solve () int res = 0 ;1 ];1 ];for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) {sort (a + 1 , a + i);int l = 1 , r = i - 1 ;while (l < r) {int mid = (l + r) >> 1 ;if (a[mid] < a[i]) l = mid + 1 ;else r = mid;int ans = abs (a[i] - a[r]);if (r + 1 >= 1 && r + 1 <= i - 1 ) ans = min (ans, abs (a[i] - a[r + 1 ]));if (r - 1 >= 1 && r - 1 <= i - 1 ) ans = min (ans, abs (a[i] - a[r - 1 ]));"\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
AC 的 set 代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <set> using namespace std;int n, res;int > s;void solve () int x;insert (x);while (--n) {auto it = s.lower_bound (x);if (it == s.end ()) {rbegin ();else if (it == s.begin ()) {begin () - x;else {auto pre = it;min (abs (x - *it), abs (x - *pre));insert (x);"\n" ;signed main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【multiset】切蛋糕
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/5581/
题意:给定一个矩形,由左下角和右上角的坐标确定。现在对这个矩形进行切割操作,要么竖着切,要么横着切。现在需要给出每次切割后最大子矩形的面积
思路:STL set。很容易想到,横纵坐标是相互独立的,最大子矩形面积一定产生于最大长度与最大宽度的乘积。因此我们只需要维护一个序列的最大值即可。对于二维可以直接当做一维来看,于是问题就变成了,需要在 log n \log n log n
删除一个数
增加一个数(执行两次)
获取最大值
如何实现呢?我们需要有序记录每一个子线段的长度,并且子线段的长度可能重复,因此我们用 std::multiset 来存储所有子线段的长度
使用 M.erase(M.find(value)) 实现:删除一个子线段长度值
使用 M.insert(value) 实现:增加子线段一个长度值
使用 *M.rbegin() 实现:获取当前所有子线段长度的最大值
由于给的是切割的位置坐标 x,因此上述操作 1 不能直接实现,我们需要利用给定的切割坐标 x 计算出当前切割位置对应子线段的长度。如何实现呢?我们知道,对于当前切割的坐标 x,对应的子线段的长度取决于当前切割坐标左右两个切割的位置 rp, lp,因此我们只需要存储每一个切割的坐标即可。由于切割位置不会重复,并且需要在 log n \log n log n std::set 来存储切割位置
时间复杂度:O ( n log n ) O(n \log n) O ( n log n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <iostream> #include <set> using namespace std;using ll = long long ;void work (int x, set<int >& S, multiset<int >& M) int >::iterator rp = S.upper_bound (x), lp = rp;insert (x);erase (M.find (*rp - *lp));insert (*rp - x);insert (x - *lp);void solve () int w, h, n;int > S1, S2;int > M1, M2;1. insert (0 ), S1. insert (w), M1. insert (w);2. insert (0 ), S2. insert (h), M2. insert (h);while (n--) {char op;int x;if (op == 'X' ) work (x, S1, M1);else work (x, S2, M2);1. rbegin () * *M2. rbegin () << "\n" ;int main () sync_with_stdio (false );tie (nullptr ), cout.tie (nullptr );int T = 1 ;while (T--) solve ();return 0 ;
【并查集】Milk Visits S
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5836
题意:给定一棵树,结点被标记成两种,一种是 H,一种是 G,在每一次查询中,需要知道指定的两个结点之间是否含有某一种标记
思路:对于树上标记,我们可以将相同颜色的分支连成一个连通块
如果查询的两个结点在同一个连通块,则查询两个结点所在的颜色与所需的颜色是否匹配即可
如果查询的两个结点不在同一个连通块,两个结点之间的路径一定是覆盖了两种颜色的标记,则答案一定是 1
时间复杂度:Θ ( n + m ) \Theta(n+m) Θ ( n + m )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 const int N = 100010 ;int n, m, p[N];char col[N];int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) {find (p[x]);return p[x];void solve () 1 );for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i++) {int a, b;if (col[a] == col[b]) {find (a)] = find (b);while (m--) {int u, v;char cow;if (find (u) == find (v)) {to_string (col[u] == cow);else {'1' ;"\n" ;
【并查集】尽量减少恶意软件的传播
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimize-malware-spread/description/
题意:给定一个由邻接矩阵存储的无向图,其中某些结点具备感染能力,可以感染相连的所有结点,问消除哪一个结点的感染能力可以使得最终不被感染的结点数量尽可能少,给出消除的有感染能力的最小结点编号
思路:很显然我们可以将当前无向图的多个连通分量,共三种感染情况:
如果一个连通分量中含有 ≥ 2 \ge 2 ≥ 2
如果一个连通块中含有 0 0 0
如果一个连通块中含有 1 1 1
当然了,由于只能移走一个感染结点,我们需要从所有只含有 1 1 1 i n i t i a l initial ini t ia l
时间复杂度:O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution {public :int p[310 ];int Find (int x) if (x != p[x]) p[x] = Find (p[x]);return p[x];int minMalwareSpread (vector<vector<int >>& graph, vector<int >& initial) int n = graph.size ();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) p[i] = i;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++)if (graph[i][j])Find (i)] = Find (j);int , pair<int , int >> ha;for (auto & x: initial) ha[Find (x)].first++;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) ha[Find (i)].second++;int , int >> v;for (auto & it: ha) v.push_back (it.second);sort (v.begin (), v.end (), [&](pair<int , int >& x, pair<int , int >& y){if (x.first == y.first) return x.second > y.second;return x.first < y.first;int idx = -1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < v.size (); i++) {if (v[i].first == 1 ) {break ;if (idx == -1 ) {return *min_element (initial.begin (), initial.end ());int res = n + 10 ;for (auto & x: initial) {int px = Find (x);if (ha[px].first == v[idx].first && ha[px].second == v[idx].second) {min (res, x);return res;
【并查集】账户合并
https://leetcode.cn/problems/accounts-merge/
题意:给定 n 个账户,每一个账户含有一个用户名和最多 m 个绑定的邮箱。由于一个用户可能注册多个账户,因此我们需要对所有的账户进行合并使得一个用户对应一个账户。合并的规则是将所有「含有相同邮箱的账户」视作同一个用户注册的账户。返回合并后的账户列表。
思路:这道题的需求很显然,我们需要合并含有相同邮箱的账户。显然有一个暴力的做法,我们直接枚举每一个账户中所有的邮箱,接着枚举剩余账户中的邮箱进行匹配,匹配上就进行合并,但这样做显然会造成大量的冗余匹配和冗余合并,我们不妨将这两个过程进行拆分。我们需要解决两个问题:
哪些账户需要合并?很容易想到并查集这样的数据结构。我们使用哈希表存储每一个邮箱的账户编号,最后进行集合合并即可维护好每一个账号归属的集合编号。O ( n m ) O(nm) O ( nm )
如何合并指定账户?对于上述维护好的集合编号,我们需要合并所有含有相同“祖先”的账户。排序去重或使用有序列表均可实现。O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O ( n log n )
时间复杂度:O ( n log n ) O(n\log n) O ( n log n )
[] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 struct dsu {int n;int > p;dsu (int _n) { n = _n; p.resize (n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i; }int find (int x) return (p[x] == x ? p[x] : p[x] = find (p[x])); }void merge (int a, int b) find (a)] = find (b); }bool query (int a, int b) return find (a) == find (b); }int block () int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) ret += p[i] == i; return ret; }class Solution {public :accountsMerge (vector<vector<string>>& accounts) {int n = accounts.size ();int >> hash;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1 ; j < accounts[i - 1 ].size (); j++) {1 ][j]].push_back (i);dsu d (n) ;for (auto & it: hash) {int > v = it.second;for (int i = 1 ; i < v.size (); i++) {merge (v[i - 1 ], v[i]);int > fa;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {insert (d.find (i));for (auto p: fa) {for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) {if (d.find (i) == p) {if (ans.empty ()) {push_back (accounts[i - 1 ][0 ]);for (int j = 1 ; j < accounts[i - 1 ].size (); j++) {insert (accounts[i - 1 ][j]);for (auto mail: se) {push_back (mail);push_back (ans);return res;
[] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class dsu :def __init__ (self, n: int ) -> None :self .n = nself .p = [i for i in range (n + 1 )]def find (self, x: int ) -> int :if self .p[x] != x: self .p[x] = self .find(self .p[x])return self .p[x]def merge (self, a: int , b: int ) -> None :self .p[self .find(a)] = self .find(b)def query (self, a: int , b: int ) -> bool :return self .find(a) == self .find(b)def block (self ) -> int :return sum ([1 for i in range (1 , self .n + 1 ) if self .p[i] == i])class Solution :def accountsMerge (self, accounts: List [List [str ]] ) -> List [List [str ]]:from collections import defaultdictlen (accounts)hash = defaultdict(list )for i in range (1 , n + 1 ):for j in range (1 , len (accounts[i - 1 ])):hash [accounts[i - 1 ][j]].append(i)for _, ids in hash .items():for i in range (1 , len (ids)):1 ], ids[i])set ()for i in range (1 , n + 1 ):for p in fa:set ()for i in range (1 , n + 1 ):if d.find(i) == p:if len (ans) == 0 :1 ][0 ])for j in range (1 , len (accounts[i - 1 ])):1 ][j])sorted (se)return res
【树状数组】将元素分配到两个数组中 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/distribute-elements-into-two-arrays-ii/description/
题意:给定 n n n A A A B B B nums[0] 到 A A A nums[1] 到 B B B nums[i],分配取决于 A A A B B B nums[i] 大的个数,最终返回两个分配好的数组
思路:首先每一个元素都需要进行枚举,那么本题需要考虑的就是如何在 log \log log
C++
法一:std::multiset<int>。可惜不行,因为统计比当前元素大的个数时,s.rbegin() - s.upper_bound(nums[i]) 是不合法的,因为 std::multiset<int> 的迭代器不是基于指针的,因此无法直接进行加减来计算地址差,遂作罢
法二:树状数组。很容易想到利用前缀和统计比当前数大的数字个数,但是由于此处需要对前缀和进行单点修改,因此时间复杂度肯定会寄。有什么数据结构支持「单点修改,区间更新」呢?我们引入树状数组。我们将数组元素哈希到 [1, len(set(nums))] 区间,定义哈希后的当前元素 nums[i] 为 x,对于当前哈希后的 x 而言想要知道两个数组中有多少数比当前数严格大,只需要计算前缀和数组 arr 中 arr[n] - arr[x] 的结果即可
Python
SortedList。python 有一个 sortedcontainers 包其中有 SortedList 模块,可以实现 std::multiset<int> 所有 log \log log O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) 题外话。LeetCode 可以进行第三方库导入的操作,某些比赛不允许,需要手搓 SortedList 模块,当然可以用树状数组 or 线段树解决 ,板子链接:https://blog.dwj601.cn/Algorithm/a_template/#SortedList
时间复杂度:O ( n log n ) O(n \log n) O ( n log n )
[] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 template <class T >class BinaryIndexedTree {private :int _n;int lowbit (int x) return x & (-x); }public :BinaryIndexedTree (int n) :_n(n) {resize (_n + 1 , 0 );void add (int pos, T x) while (pos <= _n) {lowbit (pos);T sum (int pos) {0 ;while (pos) {lowbit (pos);return ret;class Solution {public :vector<int > resultArray (vector<int >& nums) {int > copy = nums;sort (copy.begin (), copy.end ());erase (unique (copy.begin (), copy.end ()), copy.end ());int n = copy.size (), cnt = 1 ;int , int > a;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {int > v1, v2;1. push_back (nums[0 ]);2. push_back (nums[1 ]);BinaryIndexedTree<int > t1 (n) , t2 (n) ;1. add (a[nums[0 ]], 1 );2. add (a[nums[1 ]], 1 );for (int i = 2 ; i < nums.size (); i++) {int d1 = t1. sum (n) - t1. sum (a[nums[i]]);int d2 = t2. sum (n) - t2. sum (a[nums[i]]);if (d1 > d2) {1. push_back (nums[i]);1. add (a[nums[i]], 1 ); else if (d1 < d2) {2. push_back (nums[i]);2. add (a[nums[i]], 1 );else if (d1 == d2 && v1. size () < v2. size ()) {1. push_back (nums[i]);1. add (a[nums[i]], 1 );else if (d1 == d2 && v1. size () > v2. size ()) {2. push_back (nums[i]);2. add (a[nums[i]], 1 );else {1. push_back (nums[i]);1. add (a[nums[i]], 1 );for (int x: v2) {1. push_back (x);return v1;
[] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class BinaryIndexedTree :def __init__ (self, n: int ):self ._n = nself ._arr = [0 ] * (n + 1 )def _lowbit (self, x: int ) -> int :return x & (-x)def add (self, pos: int , x: int ) -> None :while pos <= self ._n:self ._arr[pos] += xself ._lowbit(pos)def sum (self, pos: int ) -> int :0 while pos:self ._arr[pos]self ._lowbit(pos)return retclass Solution :def resultArray (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]:sorted (set (nums))len (copy), 1 , {}for x in copy:1 0 ]], [nums[1 ]]0 ]], 1 )1 ]], 1 )for x in nums[2 :]:sum (n) - t1.sum (a[x]), t2.sum (n) - t2.sum (a[x])if d1 > d2:1 )elif d1 < d2:1 )elif d1 == d2 and len (v1) < len (v2):1 )elif d1 == d2 and len (v1) > len (v2):1 )else :1 )return v1 + v2
[] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution :def resultArray (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]:from sortedcontainers import SortedList1 ]), copy.deepcopy(nums[1 :2 ])for x in nums[2 :]:len (v1) - s1.bisect_right(x), len (v2) - s2.bisect_right(x)if d1 > d2:elif d1 < d2:elif d1 == d2 and len (v1) < len (v2):elif d1 == d2 and len (v1) > len (v2):else :return v1 + v2
【线段树/二分】以组为单位订音乐会的门票 🔥
https://leetcode.cn/problems/booking-concert-tickets-in-groups/
题意:给定一个长为 n ≤ 5 × 1 0 4 n\le 5 \times 10^4 n ≤ 5 × 1 0 4 0 0 0 a a a m m m q ≤ 5 × 1 0 4 q\le 5 \times 10^4 q ≤ 5 × 1 0 4
给定一个 k k k l i m lim l im i ∈ [ 0 , l i m ] i \in [0,lim] i ∈ [ 0 , l im ] m − a i ≥ k m - a_i \ge k m − a i ≥ k
给定一个 k k k l i m lim l im i ∈ [ 0 , l i m ] i \in [0,lim] i ∈ [ 0 , l im ] m × ( i + 1 ) − ∑ j = 0 i a j ≥ k \displaystyle m\times (i+1) - \sum_{j=0}^i a_j \ge k m × ( i + 1 ) − j = 0 ∑ i a j ≥ k
思路一:暴力 。
对于询问 1,我们直接顺序遍历 a 数组直到找到第一个符合条件的即可;对于询问 2,同样直接顺序遍历 a 数组直到找到第一个符合条件的即可;
时间复杂度 O ( q n ) O(qn) O ( q n )
思路二:线段树上二分 。
TODO
时间复杂度 O ( q log n ) O(q\log n) O ( q log n )
暴力代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class BookMyShow :def __init__ (self, n: int , m: int ):self .a = [0 ] * n self .n = nself .m = mdef gather (self, k: int , lim: int ) -> List [int ]:for i in range (lim + 1 ):if self .m - self .a[i] >= k:self .a[i]self .a[i] += kreturn [l, r]return []def scatter (self, k: int , lim: int ) -> bool :if self .m * (lim + 1 ) - sum (self .a[:lim+1 ]) < k:return False 0 while k > 0 :if self .m - self .a[i] >= k:self .a[i] += k0 else :self .m - self .a[i]self .a[i] = self .m1 return True
线段树上二分代码: